How Google Uses SEO For Its Websites
BY Dexter Tam

LISTEN
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of leveraging adjustments to your website, whether on the site itself or throughout the internet, to increase visibility by earning higher listing positions on search engine results pages. With Google Search being the dominant search engine in the market, almost all businesses attempt to adhere to Google’s primary recommendations of creating unique, informative content and acquiring backlinks to show authority within their respective industries.
Staying informed on news regarding Google Search and being proactive with revisions to appease Google’s search algorithm updates is a surefire way to boost traffic to your website, which in turn should lead to more conversions and new clients.
However, have you ever wondered how Google applies search engine optimization techniques to its websites? According to Sean O’Keefe, a website optimization contributor at Google, the company owns and operates over 7,000 websites, managed by hundreds of marketing and product teams globally. O’Keefe says that Google-owned websites are treated identically to every other site on the web, and that teams responsible for overseeing its sites follow the same practices as any other search marketers — the guidelines given by Google webmasters that describe how to perform well on Google Search.
O’Keefe outlines an SEO blueprint that Google’s search engine optimization teams stand by. These strategies can be applied regardless of whether or when a search algorithm update occurs, and anybody with a website can incorporate these practices for potentially increased performance on Google Search.
Start small for big results
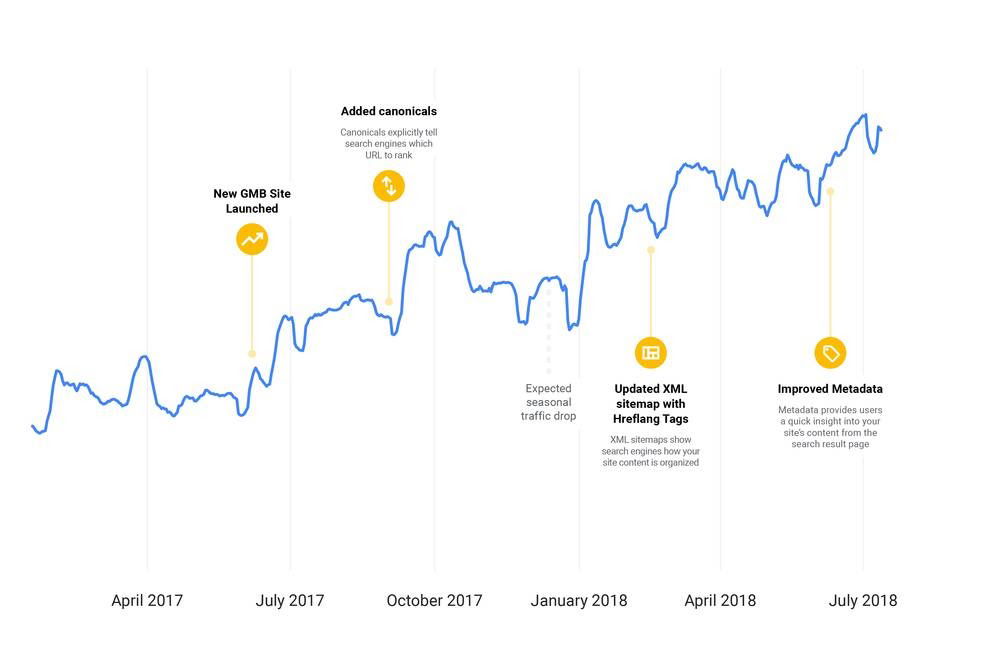
O’Keefe makes the case that small-scale, cumulative search engine optimization updates to your website can yield notable growth over time. As an example, he references the Google My Business marketing site. Following web fundamentals, with the foundation of a fast, integrated, reliable and engaging site, allowed the Google My Business website to double its organic traffic in just slightly over a year.
To go back to the basics, run a technical SEO audit on your website. This will catch small items that you can easily fix. For example, do your web pages have a clear, concise title, header tags and a meta description? Are web crawlers able to properly read your website and its corresponding pages through your sitemap? If the answer is no, making some modest adjustments could provide the catalyst that helps increase your site’s visibility on search engines.
Embrace change
As long as technology evolves, SEO will be an ever-changing industry that requires search marketers to make modifications to keep up with constant innovations regularly. Less than two decades ago, smartphones fundamentally changed the way people accessed and utilized the internet. By 2017, half of all web traffic occurred on a mobile device. In 2018, mobile web traffic surpassed desktop, acquiring 52.2 percent of the market share. Being apprehensive, whether due to a lack of technical knowledge or fear of detrimental return from change, can ultimately cause your firm’s website to stagnate as your competitors take advantage of innovation.
Because of mobile’s dominance in web traffic, firms must now optimize their websites to be as mobile-friendly as possible. Google has already adopted a mobile-first index for its search engine, meaning its search algorithms will grade pages and determine their place on search engine results pages (SERPs) based on the mobile version of your website.
Explore AMP
One of the ways Google has responded to increases in mobile traffic is through its accelerated mobile pages (AMP) project. AMP is a relatively new framework developed by Google that is designed to make mobile web pages nimble through caching and by restricting certain aspects of time-honored yet increasingly archaic markup languages, resulting in superior loading speeds.
Since most users will leave a page if it does not fully load within three seconds, embracing AMP will help keep users on your pages, thus increasing your opportunity to convert visitors to leads. Another positive benefit of having pages that load quickly is that page speed is one of the factors Google’s algorithms take into account when determining search rankings. O’Keefe provided a graph showing increased traffic of over 200 percent to the Think with Google website after AMP errors were alleviated, and the framework was able to flourish as intended.
Seek rich snippets
Another trend in Google’s search results is the growing inclusion of rich snippets in SERPs. Rich snippets are easy-to-grasp bits of information pulled directly from websites. Law firms should embrace rich snippets and work to have their page content featured in snippets.
The two types of snippets that take up real estate on a SERP are the featured snippet, and the people always ask snippet. Featured snippets are usually seen at the top of the page, above all other listings, and commonly try to provide a direct answer to the search query. The people always ask snippets show additional questions, and answers users may have, based on a particular search query.
Neither one of these rich snippets can be acquired through any means other than having the applicable content on your website to provide an answer for the specified search query. So, when you assess your content marketing strategy, look for opportunities to create informative content, and try to answer questions within your content that are relevant to popular search queries.
Adding structured data to your website is a technical SEO practice you can apply that will help Google display additional information about your firm on results pages. Web crawlers find information to display in both rich and featured snippets in a similar way: by scanning pages for relevant content that can be applied to search queries. To get a featured snippet, your page must contain content that best answers a specific question. With structured data, however, you can add code, or markups, to make the information you want to be displayed easily for web crawlers to find. These markups are known as schema. Provided you set up the schema correctly, attractive information on your website such as client reviews and frequently asked questions, may show up on SERPs under your listing.
Whenever possible, consolidate
You may think that creating multiple brands and websites is beneficial in the long-run because essentially you are cornering your practice area market with sites that are all owned by you, right? In the past, Google also believed in this principle and used this strategy to create multiple websites for slightly different marketing plans.
However, Google soon realized that having numerous websites led to similar or duplicate content, which does not positively serve users. Imagine a SERP where most of the listings had virtually the same information, sometimes even word-for-word content. That would effectively pigeon-hole users into that particular material, for better or worse.
Google believes in the availability of diverse content and letting users decide for themselves what they believe to be authoritative and relevant. Google uses the decisions users make to tinker with its algorithms in an attempt to meet users’ preferred inclinations. Now, duplicate content is considered a cardinal sin, and one of the most significant factors in Google penalizing a website or even disciplining it through a manual action.
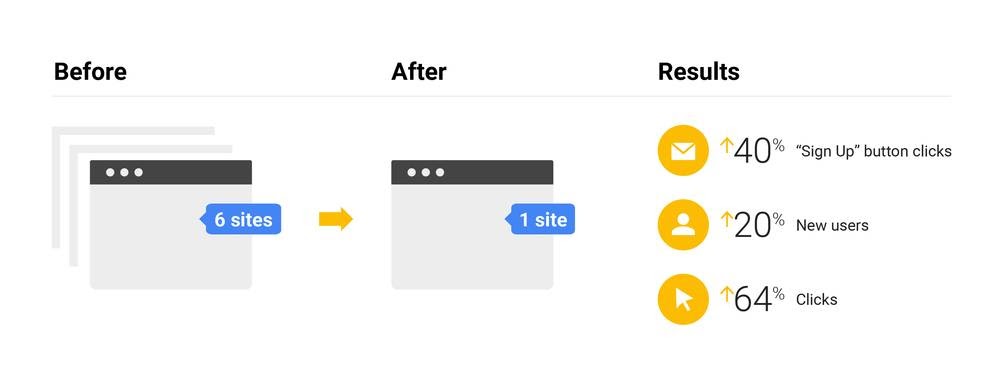
O’Keefe recommends that if you do have more than one website, that you consolidate them all into one exceptional website, rather than having various average to above-average ones. To provide context for his advice, Google Retail originally had six websites but was centralized into one site. The outcome speaks for itself:
Arguably, search engine optimization is a social science. Google’s algorithms are ever-changing, directly influenced by a trove of search behavior made by millions of users on a second-to-second basis. Incremental changes to your website, keeping up-to-date on the news regarding search engines, being fearless when adopting new features or techniques, and unifying your brand into a singular portal, are approaches Google itself takes when carrying out SEO for its websites.
LATEST STORIES