How Relevance & Authority Affect Search Results
BY Dexter Tam

LISTEN
Google facilitates 3.5 billion searches a day and 1.2 trillion searches a year worldwide. The answers are out there, the hurdle is how to best present it to consumers. Google’s solutions to this is relevance and site authority.
From the Renaissance to the Industrial Revolution to the Digital Age, we have categorized periods of time with their respective influence on society. The 21st century will be known as the Age of Information. Knowledge is now literally at our fingertips, and with 46 percent of the world having access to the Internet, many are able to be informed and educated.
Relevance
When you make any search inquiry, you want the best, most appropriate content shown to you. This is where search relevance comes into play. Based on the way you choose to formulate your queries, search engines will display results pertinent to your needs. Search engines use two types of search relevance for showing results: pure keyword and contextual relevance.
Pure keyword relevance
Pure keyword relevance is the standard way search engines analyze search queries. Taking into account what your search term is, search engines will give you what they think is the best result based on the keywords. An example of pure keyword relevance would be to search for a specific law firm and get the appropriate business information regarding that firm.
Contextual relevance
Contextual relevance is all about relatability. When you search for anything, search engines will remember what your previous queries were. For example, if you watch a video on YouTube, contextual relevance dictates that the next video up for suggestion will be something similar to what you just watched. Based on your previous results, contextual relevance will show you related topics and content. This approach is suited for consumers wanting to browse and ascertain information themselves.
Hummingbird
Hummingbird is a search algorithm implemented by Google that aims to improve contextual relevance of results. It was created in August 2013 and announced in September of the same year.
Hummingbird was developed to increase comprehension for synonyms and context. It allows Google to discern more accurately what users are looking for. This idea is known as semantic search. Instead of processing search queries word for word, a semantic search will try to understand why the user is looking for something, based on the context of the search terms. Semantic search takes into consideration things like synonyms, concept matching and natural language queries rather than just word strings.
Writing for Hummingbird
In order to better create relevant content, zero-in on your targeted audience. A more broad approach may yield more results in total throughout Google’s listings, but these results will not be ranked well.
Based on that sentiment, having content that is high valued for your particular audience will give you a better chance of ranking at the top of the search engine result page and holding visitors’ attention once they have arrived on your website. Both of these goals are key to helping improve your site’s conversion rate.
Authority
Another metric search engines use to rank websites for their search results is site authority. There are many factors that affect authority, such as page speed, related keywords, search engine optimization and design.
PageRank
PageRank is Google’s official metric for site authority. Named after cofounder Larry Page, PageRank was the first and best-known search algorithm that ranks websites on their search results. Based on a 0-10 valuation, with 10 being the highest possible score, PageRank allowed people to see how authoratative Google considers their web pages to be. Google, for example used to rate its own home page at 10.
However, because of manipulation to PageRank through black-hat seo methods like selling links and keyword stuffing, Google announced on April 15, 2016 that they have closed PageRank data to the public. This is an attempt to keep PageRank score impartial and organic.
Post-PageRank authority
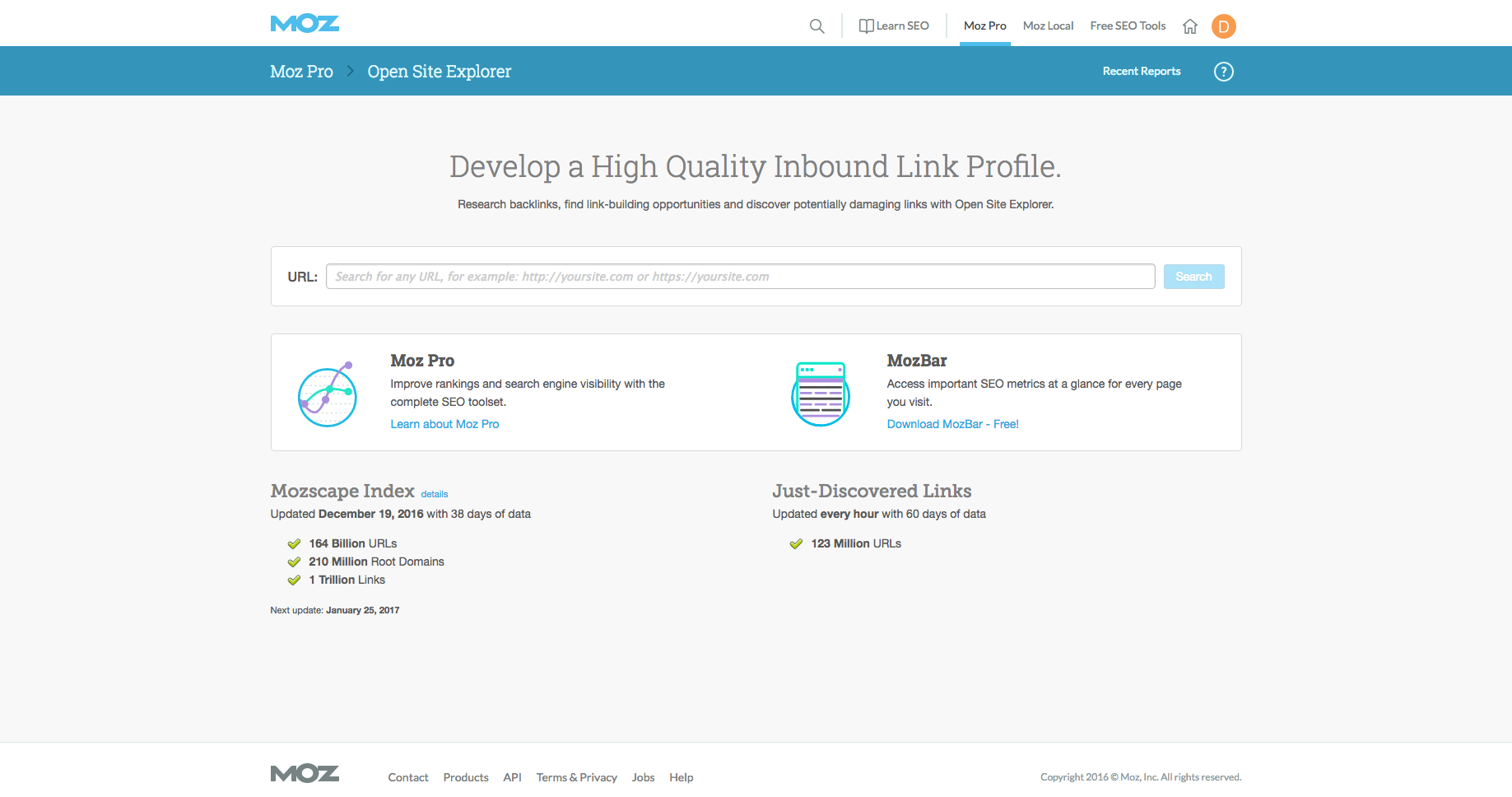
Now that PageRank is no longer publicly visible, Moz’s Open Site Explorer has emerged as a substitute. Simply plug an URL in, and you will see Moz’s calculation of Page and Domain Authority. Page Authority is merited based on the strength of the respective page. Domain Authority is gathered from the entire website. Moz uses its own metrics and scores their authority from 0-100.
Open Site Explorer also offers a wide array of data about links, including inbound links, linking domains, anchor text and a metric it refers to as just discovered links. The tool also lets you compare link metrics and look for new linking opportunities. While Moz does not reveal the secret of how it calculates Page and Domain Authority, the measurement is likely based heavily on link portfolios and link activity.
Among the search engine optimization techniques available, links are perhaps the most important factor of influence. Links are a vote of confidence for your website. Your best bet to increase site authority would be to have another website that is highly valued link your content to their site. However, this must happen organically, or you risk violating Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. Link building is possible, and effective, when handled carefully.
LATEST STORIES



